The
principles of art are rules
or guidelines that are to be
considered when judging art. The principles are:
repetition, variation, contrast, balance, proportion,
emphasis, pattern, and unity.
REPETITION (PATTERN / RHYTHM):
Yayoi Kusama
Pattern
and rhythm (also known as repetition)
is consistency with colors and lines.
Putting a red spiral at the bottom left and
top right, for example will cause the eye to
move from one spiral to the other. It is indicating
movement by the repetition of elements.
Rhythm makes an artwork seem active.
a. Rhythm – Recurring elements
Regular Rhythm – same elements
Irregular Rhythm – Similar elements
b. Harmony – Logical repetition
c. Dissonance – Illogical repetition
d. Pattern

Muslim Architecture
FRACTALS
www.enchgallery.com
Repetition and simplification in the music Ready Steady Go
by Paul Oakenfold:
Collateral Club Scene.
VARIATION / VARIETY
Variety
is the quality of having different forms or
types. The differences give a design visual
and conceptual interest: notably use of
contrast, emphasis, difference in size and
color.
CONTRAST
Contrast
show differences and diversity in an artwork
by combining elements to create interest.
Contrast provides an artwork with something
interesting to break the repetitions.
In the first two measures of Bach's
Invention No. 8 in F major you can find
every contrast in music. In the first
measure we have notes against silence. In
the second measure we have the notes in the
right hand being played twice as fast,
attached (legato), and going down in pitch.
In the left hand, we have notes being played
twice as slow, detached (staccato), and
going up in pitch.
Listen:
Ryan Layne Whitney -
Bach:
Invention No. 8 in F major, on clavichord
Bach: Inventions on
Violin and Cello

BALANCE (p102)
Balance
is arranging elements so that no one part of
a work overpowers, or seems heavier than any
other part. Two different kinds of balance
are:
a. Symmetrical Balance
b. Asymmetrical Balance
Types of Symmetrical Balance:
- Radial Symmetry

Plate from Ernst
Haeckel's Kunstformen der Natur.
These sea anemones display
radial symmetry.
-
Pentamerism
Pentamerism is a variation of
radial symmetry. These are arrangements of equal parts
around a central axis.

- Bilateral Symmetry

In bilateral symmetry (also
called plane symmetry) two mirrored halves can be referred
to as the right and left.
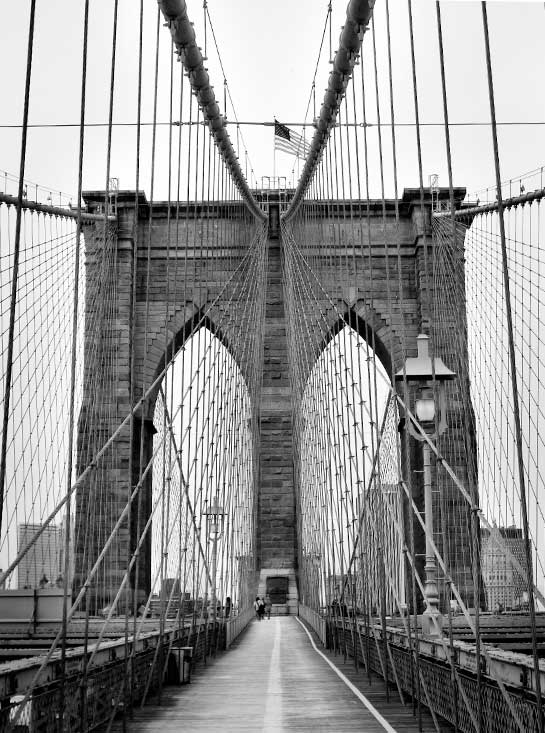

The Brooklyn Bridge is a
great example of symmetry, repetition, and line. Notice the
two gothic arches - and the keystone at the top of each
arch.
- Asymmetric
No
symmetry is called
asymmetric.
PROPORTION
Proportion
is the size relationship of forms and
shapes. Good proportion causes a sense
of unity and harmony.
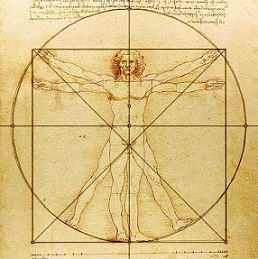
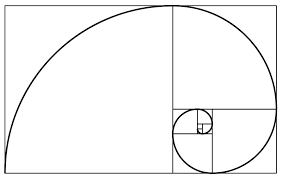
Fibonacci
Spiral

Human Body Image
II
Francesco Di Giorgio Martini
Francesco di Giorgio Martini (1439 – 1502) was an Italian
painter, sculptor, architect, and military engineer who
built almost seventy fortifications.



EMPHASIS / FOCAL POINT
Emphasis
(also called focal point) is where the focus
is concentrated through design principles or
meaning. To do this one develops points of
interest to pull the viewer's eye to
important parts of the work. It is to make
one part of an artwork dominant. It makes an
element or object in a work stand out. To
use emphasis in an artwork is to attract the
viewer's eyes to a place of special
importance in a artwork.
UNITY
Unity
or harmony is the quality of
wholeness or oneness that is achieved
through the effective use of the elements
and principles of art. It is the arrangement
of elements and principles to create a
feeling of completeness.

